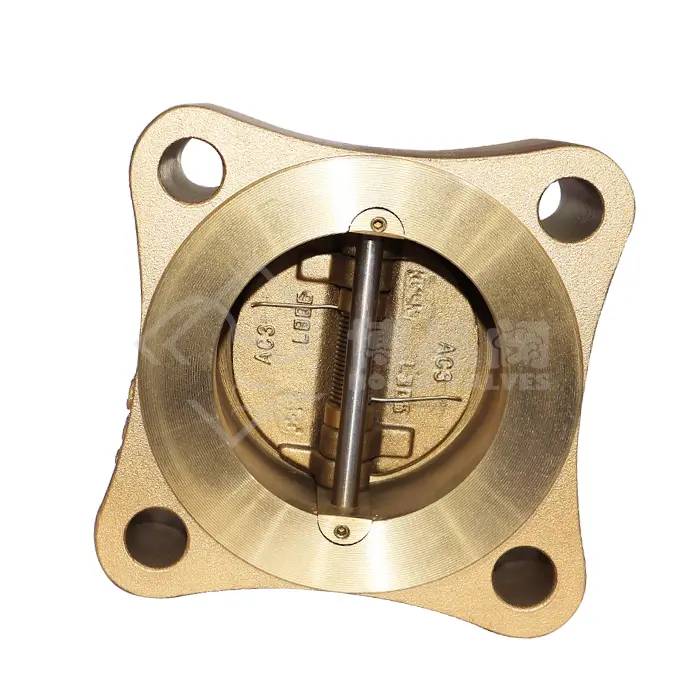
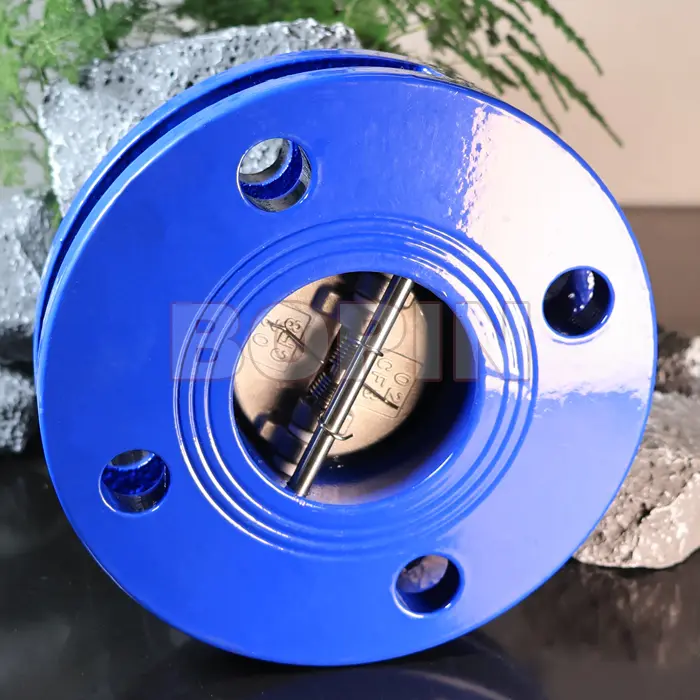
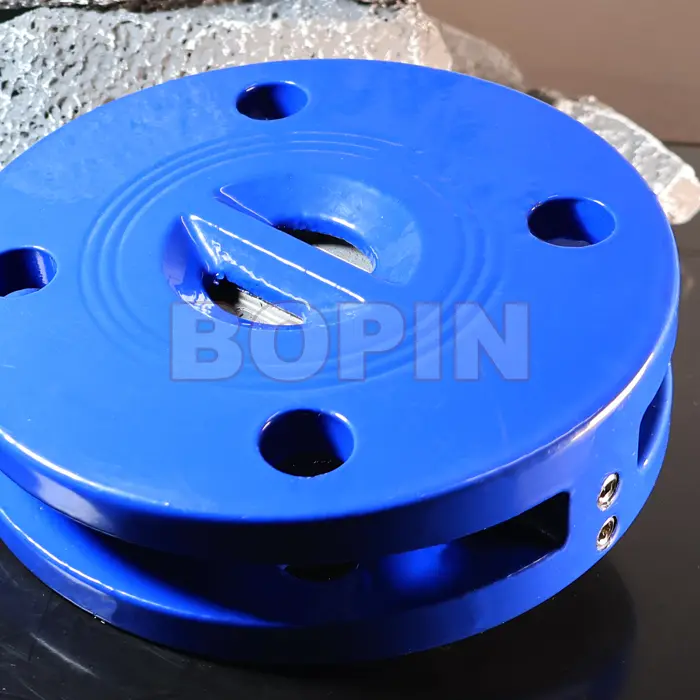
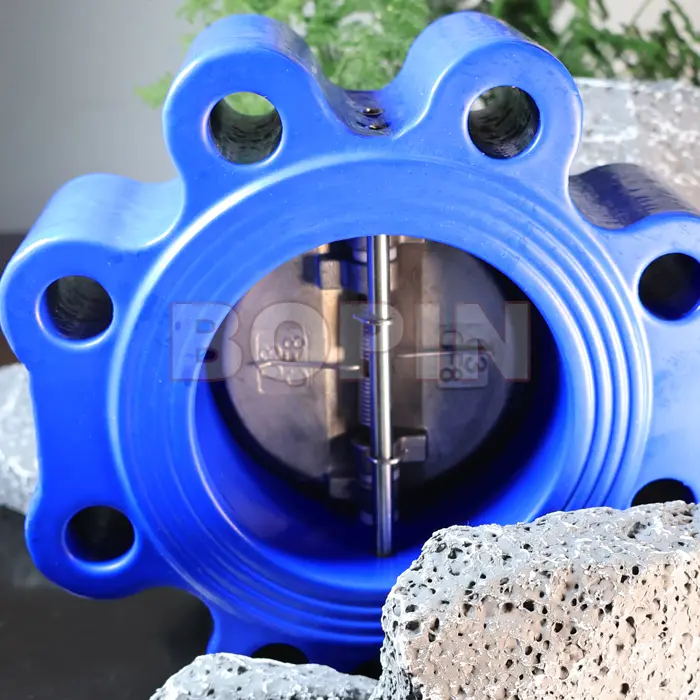
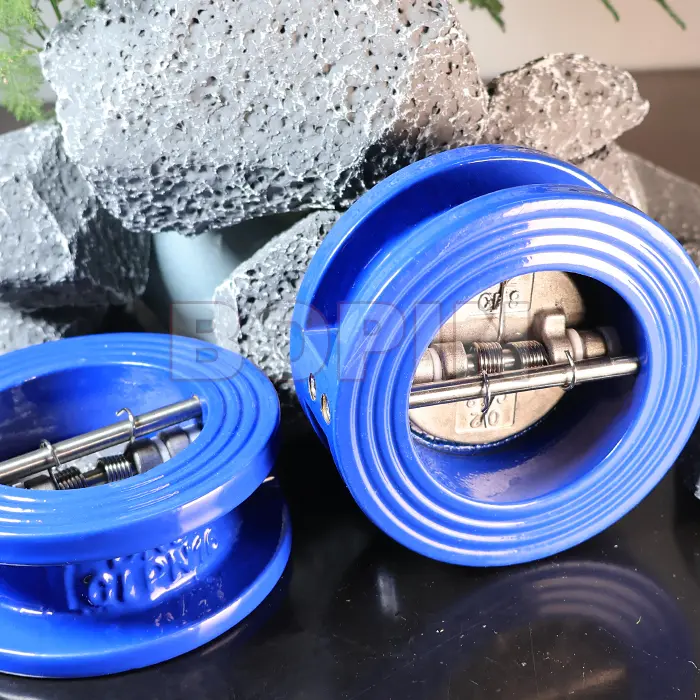
Cast Iron Wafer Type Dual Plate Check Valve
Technical Requirement
Design and Manufacture acc. to API594
Face to Face Length acc. to API 594 / ANSI B16.10 / DIN 3202 / BS 1868 / ISO 5752
Flange Drilling acc. to ANSI B16.1 / ANSI B16.5 / DIN 2501 / JIS B 2220
Hydraulic Test acc. to API594
Production Range
Pressure: PN10/16
Material: GG25
Diameter: DN15 to DN1500
Features
Material: Made of cast iron, which is a strong, durable, and corrosion-resistant material, often chosen for its cost-effectiveness and ability to withstand various fluids and pressures.
Dual Plate Design: Instead of a single flap or disc, the valve has two plates that pivot open and closed.
Reduced pressure drop: Dual plates can open more freely and reduce resistance to fluid flow.
Faster response: The dual plates close quickly when there is backflow, minimizing the risk of damage from reverse pressure.
Types of Cast Iron Dual Plate Check Valves
There are several types of Cast Iron Dual Plate Check Valves, each designed for specific applications and operating conditions. The types typically vary based on factors like design, installation orientation, and the way they handle flow, pressure, and materials. Below are some common types:
1. Wafer Type Dual Plate Check Valve
Design: This valve has a compact, wafer-like design with two plates that hinge inward to allow fluid to flow in one direction.
Installation: Installed between two flanges with no need for additional housing or casing.
Advantages:
Space-efficient and lightweight.
Simple to install in tight spaces.
Applications: Used in pipeline systems with limited space and where the flange-to-flange connection is preferred.
2. Lug Type Dual Plate Check Valve
Design: The lug type has threaded lugs on both sides of the valve body, which allows it to be bolted into a system. These lugs can be used to mount the valve between flanges.
Installation: It can be installed between flanged pipe connections but does not require bolts through the entire valve body.
Advantages:
Easier to replace or maintain without removing the entire valve body from the pipeline.
Can be installed in a line under pressure on one side.
Applications: Common in installations where frequent maintenance or isolation is needed.
3. Flanged Type Dual Plate Check Valve
Design: The flanged type has flanges on either side of the valve body, making it suitable for bolting directly to the pipeline.
Installation: Requires bolting through the flanges, typically used in systems where a strong connection is necessary.
Advantages:
Ideal for high-pressure applications.
Offers a stronger connection compared to the wafer and lug types.
Applications: Used in industrial applications with high-flow systems or high-pressure conditions.
4. Spring-Loaded Dual Plate Check Valve
Design: A spring-loaded version incorporates a spring mechanism to assist in the closure of the dual plates when flow stops or reverses.
Installation: This type can be installed horizontally or vertically.
Advantages:
Faster closure due to the spring assistance.
Can be more effective in preventing backflow in applications where flow reversal can happen quickly.
Applications: Common in pumping stations, sewage systems, and other environments where backflow needs to be prevented rapidly.
5. Inline Type Dual Plate Check Valve
Design: This valve type is installed directly inline within the pipe system.
Installation: It can be installed in both vertical and horizontal pipelines, with the body typically designed for straightforward piping configurations.
Advantages:
Simple design for easy installation.
Effective for pipelines where there is a requirement to prevent backflow or reverse pressure.
Applications: Used in general industrial applications like water systems, HVAC, and other fluid-handling processes.
6. Tilting Disc Dual Plate Check Valve
Design: Similar to dual plate valves but with plates that tilt or swing open at an angle. The plates rotate around a central pivot point.
Advantages:
Low-pressure drop and quick response to reverse flow.
Applications: Typically used in large industrial systems and applications where precise backflow prevention is critical.
7. Silent Type Dual Plate Check Valve
Design: A variation designed with noise-reducing features, such as special cushioning or mechanisms to reduce the impact of the plates slamming shut.
Advantages:
Reduces the slamming noise that occurs when the plates close, which can be a concern in large systems.
Often includes a damping mechanism to slow the plate closure.
Applications: Frequently used in residential or commercial water supply systems, or any application where noise reduction is important.
8. Heavy Duty Cast Iron Dual Plate Check Valve
Design: Designed for higher pressures and more demanding applications, these valves are made of thicker, more robust cast iron and are built to handle more strenuous conditions.
Advantages:
Suitable for high-pressure, high-flow environments.
More durable in harsh industrial conditions.
Applications: Often used in large-scale industrial plants, sewage treatment plants, and power generation systems.
9. Corrosion-Resistant Dual Plate Check Valve
Design: Made with special alloys or coatings to resist corrosion from harsh chemicals, acids, or other aggressive fluids.
Advantages:
Enhanced resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for aggressive fluid handling.
Applications: Used in chemical processing, water treatment, or marine applications.
10. Turbine Type Dual Plate Check Valve
Design: Features a turbine-style mechanism inside that controls the movement of the dual plates.
Advantages:
Provides a smoother, more controlled closure.
Applications: Often used in high-flow and high-speed applications where a precise valve operation is required.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Type:
Flow Rate: Some designs handle higher flow rates better than others.
Pressure: Make sure the valve can withstand the operating pressure of the system.
Space Constraints: Consider the available installation space for the valve type.
Maintenance: Some types, such as the lug or flanged types, are easier to maintain and replace.
Environment: For corrosive or high-temperature fluids, choose a valve with corrosion-resistant features or a high-temperature design.
Each type of cast iron dual plate check valve has its specific advantages and applications, and selecting the right one depends on the specific needs of the fluid system and operating conditions.
Advantages
Compact Design: The dual plate mechanism allows the valve to be more compact than other types of check valves with larger single discs.
Improved Performance: The dual plates can operate more efficiently under higher flow rates, reducing turbulence and vibrations.
In summary, a Cast Iron Dual Plate Check Valve is an effective solution for controlling fluid flow direction and preventing backflow in a variety of industrial and commercial applications.
Applications
Typically used in systems where backflow must be prevented, such as in pipelines, pumps, and water treatment facilities.
Common in industrial, municipal, and commercial fluid systems.