+86 19720579616

+86 19720579616

 Zalo
Zalo

In the realm of industrial applications, choosing the right forged steel valves is crucial. Industry expert John Smith has emphasized, "The right valve can make or break a project." Understanding this is key for engineers and procurement specialists.
Forged steel valves offer significant advantages. They are durable, resistant to high pressures, and suitable for various fluids. However, the selection process can be challenging. Different projects have unique requirements. Some may demand resilience, while others prioritize cost-effectiveness.
Details matter when selecting forged steel valves. Considerations like size, pressure rating, and material compatibility are essential. It’s easy to overlook these specifics. An improper choice can lead to failure. Reflecting on past experiences can guide better decisions. Each valve selection should not just focus on performance, but also on the risks involved.

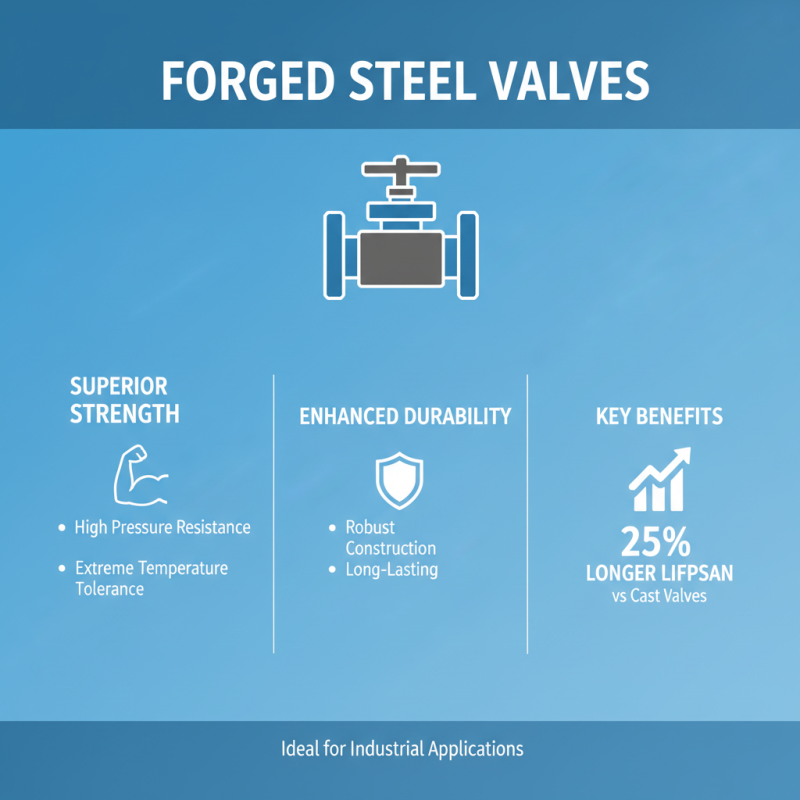
When selecting forged steel valves, understanding their key features is crucial. These valves are known for their excellent strength and durability. They can withstand high pressure and extreme temperatures, making them ideal for various industrial applications. According to recent industry reports, forged steel valves can last up to 25% longer than cast valves under similar conditions.
One significant advantage of forged steel valves is their superior leak resistance. The forging process creates a denser material, reducing the likelihood of micro-cracks. This characteristic is essential for applications requiring high reliability. However, not all forged steel valves are created equal. It's important to assess the specific type of steel used, as different grades offer varied performance metrics.
Tips: Always check the valve’s pressure rating and temperature limits. Ensure they align with your project's requirements. Remember, incorrect specifications can lead to failures.
Another feature worth noting is the ease of maintenance. Forged steel valves typically require less frequent repairs. This can lead to a reduction in operational downtime. However, carefully consider your application type before making a selection. A common mistake is assuming all forged steel valves are suitable for all environments. Each application has unique requirements that can impact valve performance and longevity.
When selecting forged steel valves, industry standards play a crucial role. ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) and ANSI (American National Standards Institute) specifications provide essential guidance. These standards ensure quality, safety, and performance. For example, ASTM A105 covers carbon steel valves, while ANSI B16.34 outlines the design and construction.
Understanding these specifications is vital for your project. ASTM data states that carbon steel valves offer excellent mechanical properties. Yet, they may corrode if not properly maintained. It's essential to consider environmental factors. A valve that works in one setting may fail in another. ANSI specifications illustrate pressure classes and temperature ratings. These details are critical to ensure the valve operates correctly under the intended conditions.
Another aspect is compatibility with fluids. Not all valves handle the same materials. Some may weaken when exposed to harsh chemicals. Regular testing is advisable to prevent unexpected failures. A reported 15% of valve failures stem from compatibility issues, highlighting the importance of diligent selection. Careful evaluation of ASTM and ANSI specifications can help mitigate risks and enhance performance.
When selecting forged steel valves, application requirements are crucial. Pressure is one of the first factors to consider. Commonly, valves face pressure ranges from 150 psi to over 3,000 psi. For example, the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) suggests that valves need to sustain pressures according to their ratings. If you overlook this, you risk valve failure, potentially causing system leaks or shutdowns.
Temperature also plays a vital role. Forged steel valves operate well in extreme conditions, typically up to 800°F. However, exceeding this could compromise the valve’s integrity. Many industries report that high temperatures can accelerate wear or corrosion if not correctly assessed. Assess your working environment to ensure your valves can withstand thermal stress.
Tips: Always refer to the valve's pressure-temperature rating charts. This can prevent choosing the wrong valve and save costs. Additionally, consider the type of media the valve will handle. For corrosive media, coatings may be necessary. Not all valves suit every media type. Understanding both pressure and media properties can drastically minimize maintenance issues and enhance performance.
When selecting forged steel valves, material choice is crucial. Different alloys have unique properties that affect performance.
Stainless steel, for instance, offers excellent corrosion resistance. However, its strength can be lower compared to other materials. In contrast, carbon steel valves provide superior strength but are more susceptible to rust. Depending on the environment, this can be a significant drawback.
According to industry reports, the choice of alloy influences valve life span and efficiency. For example, valves made from high-grade alloys reduce maintenance costs by 30%. On the other hand, using low-quality materials can lead to premature failure. This failure can disrupt operations and lead to financial losses. Many plants still overlook these details, focusing only on initial costs rather than long-term benefits.
In some cases, the specific application dictates the alloy. In high-pressure systems, duplex stainless steel may be ideal. Yet, it is often underutilized due to higher upfront costs. Many decision-makers remain hesitant, lacking awareness. Ultimately, understanding the impact of material choices is not just an option; it is essential for optimal performance.
When selecting forged steel valves, cost and quality must be balanced carefully. A low price can be tempting but may lead to issues later. Valve failures can result in costly repairs and downtime. Consider the specific needs of your application before rushing into a decision.
Tips for making a cost-benefit analysis: Evaluate the lifespan of the valve. Expensive models may have longer durability. Sometimes, investing more upfront saves money over time. Research the materials used in the valve construction. High-quality steel can withstand corrosive environments better, reducing maintenance costs.
It’s also critical to assess the warranty offered. A solid warranty signifies confidence in the product. If a valve fails under warranty, it can save on replacement costs. However, if the warranty is lacking, it could lead to unnecessary expenses. Making an informed choice requires careful consideration of both quality and price, and revisiting your priorities now and then is essential.
| Valve Type | Material Quality | Price Range (USD) | Pressure Rating (PSI) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gate Valve | A105 | $250 - $450 | 150 - 2000 | Water, Oil, Gas |
| Globe Valve | A182 F316 | $300 - $600 | 150 - 1500 | Steam, Water, Fuel |
| Ball Valve | A234 WPB | $200 - $500 | 150 - 3000 | Oil, Gas, Chemical |
| Check Valve | A105 | $150 - $400 | 150 - 2000 | Water, Oil |
| Plug Valve | A105 | $300 - $550 | 150 - 1500 | Oil, Gas |